-
Reorientational Hydrogen Dynamics in Complex Hydrides with Enhanced Li + Conduction
T. Burankova, L. Duchêne, Z. Lodziana, B. Frick, Y. Yan, R.-S. Kühnel, H. Hagemann, A. Remhof and J.P. Embs
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 121 (33) (2017), p17693-17702


DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b05651 | unige:96311 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF | Supporting Info
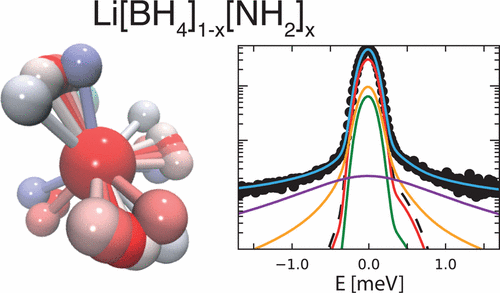
Lithium amide–borohydrides Li[BH4]1–x[NH2]x possess liquid-like Li superionic conductivity at nearly ambient temperature. The fast Li+ diffusion facilitated by the localized motions of the anions is proposed to occur through a network of vacant tetrahedral sites, acting as conduction channels. To study the reorientational dynamics of the anions, we have performed quasielastic neutron scattering experiments on samples with different compositions (x = 2/3, 0.722, 0.737, 3/4) over a broad temperature and time range. To unambiguously disentangle the contributions of the two species, [BH4]− and [NH2]−, we took advantage of deuterium labeling and could clearly demonstrate that the quasielastic broadening is mainly determined by the [BH4]− reorientations. With the help of a newly developed model, supported by ab initio molecular dynamics calculations, we have identified three relaxation components, which account for generally anisotropic C3-rotations of the [BH4]− tetrahedra including jumps by a small angle from the equilibrium position.
